Predetermined Overhead Rate Calculator & Formula Online Calculator Ultra

The predetermined overhead rate is used to price new products and to calculate variances in overhead costs. Variances can be calculated for actual versus budgeted or forecasted results. One of the advantages of predetermined overhead rate is that it can help businesses monitor overhead rate. what is accounts receivable what kind of account is accounts receivable This comparison can be used to monitor or predict expenses for the next project (or fiscal year). In other words, using the POHR formula gives a clearer picture of the profitability of a business and allows businesses to make more informed decisions when pricing their products or services.
Estimating Overhead Costs
- A number of possible allocation bases are available for the denominator, such as direct labor hours, direct labor dollars, and machine hours.
- It’s a completely estimated amount that changes with the change in the level of activity.
- The predetermined overhead rate, also known as the plant-wide overhead rate, is used to estimate future manufacturing costs.
- Carefully tracking overhead expenses is key for small businesses to optimize costs.
By properly calculating and applying overhead rates, businesses can accurately assess the true costs of their operations. Traditionally, overheads have been absorbed in the product cost based on a single basis of apportionment. For instance, in a labor-intensive environment, labor hours were used to absorb overheads. On the other hand, the machine hours were used to absorb overheads in a machine incentive environment.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
The concept is much easier to understand with an example of predetermined overhead rate. For instance, imagine that your company has a new job coming up, and you need to calculate predetermined overhead rate for an estimate of manufacturing costs. Using the predetermined overhead rate formula and calculation provides businesses with a percentage they can monitor on a quarterly, monthly, or even weekly basis.
Simplify Any Calculation With Sourcetable
With features tailored for easy calculation and the ability to test these on AI-generated data, Sourcetable makes it easier and quicker to apply overhead rates in various scenarios. Manufacturers use the predetermined overhead rate to monitor and control manufacturing expenses, aligning them more closely with production outputs and sales volumes. This guide will delve into the steps to compute the predetermined overhead rate, explaining its importance for efficient budgeting and cost control in manufacturing.
Now that all parts of the equation are determined let’s calculate the predetermined overhead rate. The activity driver, also known as the allocation base, is the factor used to assign overhead costs to products. This could be machine hours, labor hours, or any other measure that reflects the use of manufacturing resources. Begin by estimating the total manufacturing overhead costs for the period. This includes all costs related to the production process that are not direct materials or direct labor. Common components are the salaries of factory managers, factory rent, property taxes, and depreciation.
Calculating Predetermined Overhead Rates Made Easy
Unexpected expenses can be a result of a big difference between actual and estimated overheads. Assume that management estimates that the labor costs for the next accounting period will be $100,000 and the total overhead costs will be $150,000. This means that for every dollar of direct labor cost a production process uses, it will use $1.50 of overhead costs. The predetermined overhead rate formula is calculated by dividing the total estimated overhead costs for the period by the estimated activity base. A predetermined overhead rate is an allocation rate that is used to apply the estimated cost of manufacturing overhead to cost objects for a specific reporting period. This rate is frequently used to assist in closing the books more quickly, since it avoids the compilation of actual manufacturing overhead costs as part of the period-end closing process.
Use the following data for the calculation of a predetermined overhead rate. Therefore, this predetermined overhead rate of 250 is used in the pricing of the new product. The overhead rate affects pricing by showing how much you need to cover your costs. If your rate is high, you may need to increase your prices to maintain profit margins. Setting overhead budgets and benchmarks for each department also helps control spending. If costs rise above predetermined limits, action can be taken to reduce expenses.
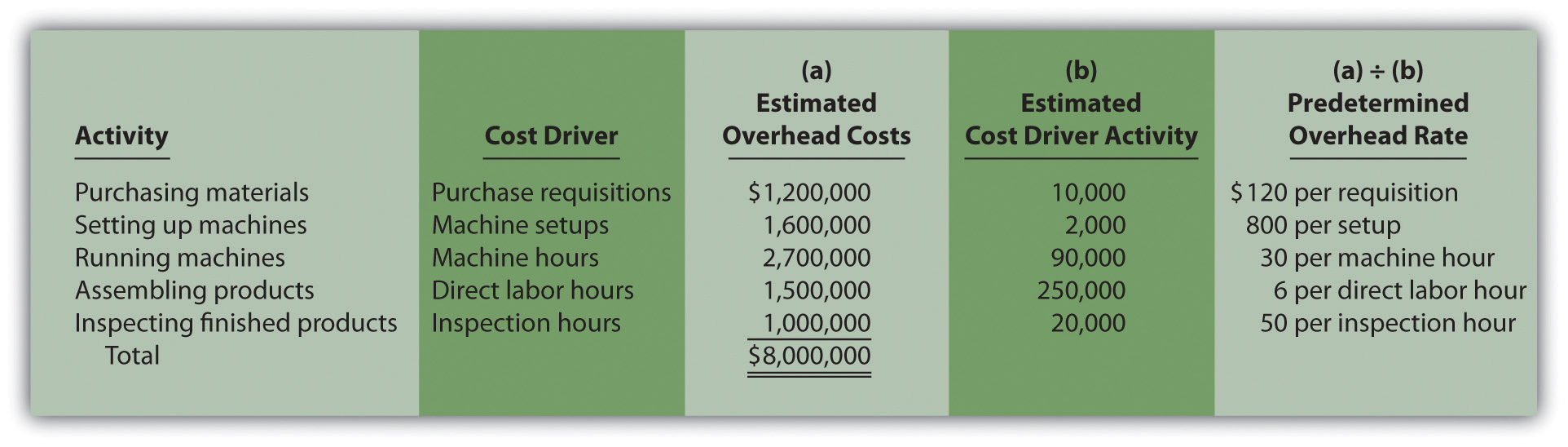
As a result, the overhead costs that will be incurred in the actual production process will differ from this estimate. The activity base (also known as the allocation base or activity driver) in the formula for predetermined overhead rate is often direct labor costs, direct labor hours, or machine hours. The activity base can differ depending on the nature of the costs involved. That is, a number of possible allocation bases such as direct labor hours, direct labor dollars, or machine hours can be used for the denominator of the predetermined overhead rate equation.
There are concerns that the rate may not be accurate, as it is based on estimates rather than actual data. In addition, changes in prices and industry trends can make historical data an unreliable predictor of future overhead costs. Finally, using a predetermined overhead rate can result in inaccurate decision-making if the rate is significantly different from the actual overhead cost. Having an accurate predetermined overhead rate helps companies better understand the full cost of production and set appropriate pricing levels.
